The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a fascinating and intricate network within the human body that plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and harmony. Comprising of receptors, enzymes, and endocannabinoids, this system has been a subject of growing interest in the realms of medicine and wellness.
What is the Endocannabinoid System?
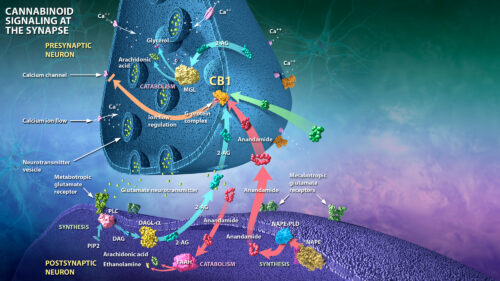
At its core, the ECS is a regulatory system, influencing a wide array of physiological processes such as mood, sleep, appetite, and immune response. The two primary types of receptors, CB1 and CB2, are found throughout the body, with CB1 concentrated in the central nervous system and CB2 predominantly in immune cells. Endocannabinoids, the messengers of the ECS, are naturally produced by the body. Anandamide, often referred to as the “bliss molecule,” and 2-AG are two prominent endocannabinoids. They act like a key fitting into the lock of cannabinoid receptors, triggering various responses.
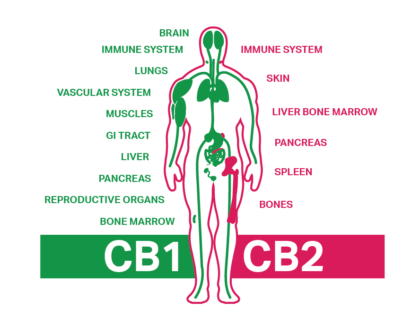
Internal vs. External Cannabinoids
Interestingly, the ECS doesn’t just respond to internal cannabinoids but also interacts with external cannabinoids, such as those found in the cannabis plant. THC, the psychoactive compound in marijuana, mimics the actions of anandamide, binding to CB1 receptors and producing its well-known effects. As research on the endocannabinoid system progresses, scientists are delving into the potential therapeutic applications of modulating its activity. Cannabinoids derived from the cannabis plant, such as CBD (cannabidiol), have gained popularity for their non-psychoactive nature and purported health benefits. CBD interacts with the ECS but does not bind directly to CB1 or CB2 receptors.
ECS and Me
Understanding the ECS has led to groundbreaking developments in medicine. Researchers are exploring its potential role in managing conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, and inflammation. Furthermore, the ECS is being investigated for its impact on neurodegenerative diseases and even as a target for cancer therapies. The introduction of cannabinoids, such as THC and CBD, has been found to influence the system in more indirect ways. This can lead to anti-inflammatory and calming effects that have shown promise in addressing conditions like anxiety, epilepsy, and chronic pain. Maintaining ECS balance is crucial for overall health. Lifestyle factors, including diet, exercise, and sleep, can influence its function. Additionally, cannabinoid-rich foods, like those containing omega-3 fatty acids, may support a healthy ECS.
The endocannabinoid system’s influence extends beyond physical health, reaching into the realms of mental well-being. Studies suggest that an imbalanced ECS may contribute to mood disorders, and researchers are exploring how targeting the system could offer novel approaches to treating conditions like depression. This intersection between neurobiology and mental health highlights the ECS’s intricate role in maintaining the delicate equilibrium necessary for our overall wellness.
The endocannabinoid system is a captivating aspect of human biology, with far-reaching implications for both medicine and well-being. As we continue to unravel its complexities, the potential for harnessing its therapeutic benefits becomes increasingly evident. From its role in regulating basic bodily functions, to its impact on mental health, the ECS stands as a testament to the interconnectedness of our biological systems and the untapped potential that lies within the delicate balance it seeks to maintain.